Introduction
In the era of digital transformation, large companies face the need to unify their internal systems, data, and communication tools in a single environment. Fragmented information and disconnected workflows can reduce productivity, and lead to inefficiencies in all departments. To address these challenges, many enterprises implement an enterprise portal — a corporate platform that provides employees with unified access to information, tools, and applications.
An enterprise portal serves as the digital gateway to all company resources. It connects teams, automates routine processes, and makes sure that every team can quickly find and share data. In this article, we will explore what an enterprise portal is and describe the main advantages of enterprise portal software. We will also highlight what distinguishes enterprise portals from small business portals and explain how companies can implement enterprise portal solutions to achieve higher performance.
One of the most well-known platforms used to create and manage enterprise web portals is Microsoft SharePoint, available in both Online and On-Premises versions. Additionally, we will review several Virtosoftware tools that extend SharePoint’s capabilities and help companies build more interactive enterprise portal systems for their specific needs.
1. Enterprise Portal: Purpose, Functions, and Goals
1.1 Definition and Purpose
What is meant by enterprise portal? In simple terms, an enterprise portal is a centralized web platform that provides employees, partners, and clients with unified access to corporate applications, internal systems, documents, and company news. This digital workspace brings together all tools and resources into a single interface.
Unlike ordinary websites or file storage systems, an enterprise portal acts as a single point of entry to corporate data, processes, and communications. It becomes the main digital environment where employees can perform daily tasks — from approving documents and tracking task progress to checking corporate news and receiving notifications about events.
Enterprise portals are often built on large-scale platforms such as Microsoft SharePoint, which offers high flexibility, advanced integration capabilities, and security features. These qualities make SharePoint a perfect foundation for enterprise portal software in organizations that require compliance and connectivity across departments.
For example, a typical employee accessing an enterprise web portal can instantly see a personalized dashboard with the team’s meeting calendar, project tasks from Microsoft Planner, news updates, shared documents stored in SharePoint libraries, and chat notifications from Microsoft Teams — all in one place, without switching between apps.
The primary goal of an enterprise portal is to simplify access to the right information while improving the transparency of internal operations. By consolidating corporate content, apps, and communications into a single ecosystem, enterprise portal solutions allow companies to accelerate decision-making, and create a connected workplace.
1.2 Core Functions and Key Features
An enterprise portal is a multifunctional space designed to adapt to the needs of each organization. Depending on your priorities, it can serve as a company intranet, a project management platform, a knowledge base, or a place for external collaboration with clients and partners. Modern enterprise portal software unites these roles, forming a single environment that supports communication and knowledge management.
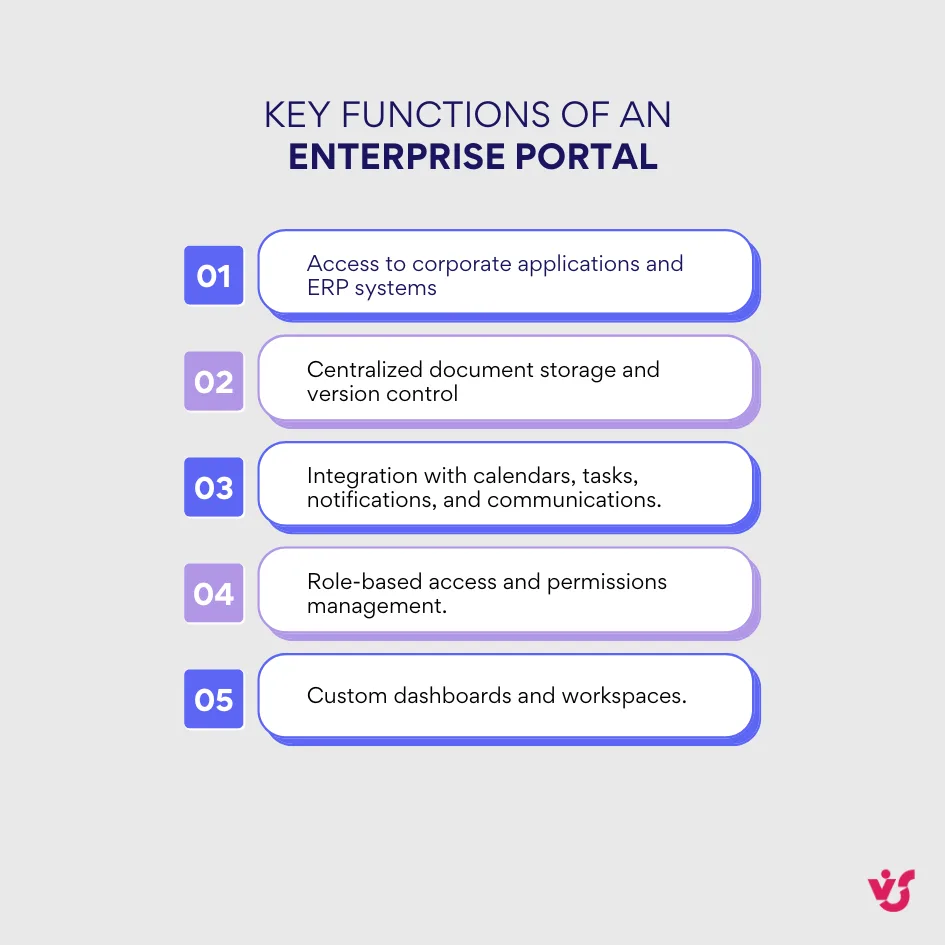
Typical functions of an enterprise portal include:
- Access to corporate applications and ERP systems. The portal integrates with tools such as Microsoft 365, CRM, HR, and BI platforms. It enables seamless access to all applications and data through a single interface.
- Centralized document storage and version control. Employees can store and co-author documents in real time while maintaining version history and access permissions for smooth collaboration.
- Integration with calendars, tasks, notifications, and internal communications. Enterprise portals consolidate daily workflows, helping staff plan activities, track deadlines, and stay informed about corporate events.
- Role-based access and permissions management. The system provides flexible configuration for different user categories — executives, internal teams, contractors, and partners — guaranteeing security.
- Custom dashboards and workspaces. Departments and project teams can build their own pages with selected widgets and documents that support their business needs.
What are the different types of enterprise portals? Generally, they fall into three main categories:
- Intranet portals are intended for internal users. They serve as a hub for document exchange, task management, employee training, and communication.
- Extranet portals are used to interact with external stakeholders such as partners, clients, and suppliers. They act as a secure place for sharing files and project data.
- Hybrid portals combine internal and external functionality, allowing organizations to manage communication both inside and outside the company within an integrated system.
In addition to these features, an enterprise web portal often includes reporting, interactive dashboards, and business process automation. As a result, enterprise portal solutions evolve from simple information hubs into platforms for enterprise-wide management and decision-making.
1.3 Why Businesses Need an Enterprise Portal
In large organizations, the volume of information, documents, tools, and communication channels grows constantly. Without proper structure, this fragmentation leads to delays and data loss. An enterprise portal solves this challenge by bringing all resources together into a unified ecosystem.
Enterprise portals help companies address several tasks:
- Transparency and faster decision-making. Managers and employees can access real-time data and see up-to-date task statuses, which speeds up coordination.
- Reduced time spent searching for information. Single data storage and intelligent document search make it easy to locate files, reports, and apps quickly without switching between systems.
- Simplified cross-department communication. The enterprise portal unites interaction channels such as news feeds, task lists, notifications, calendars, and threads, improving collaboration between teams.
- Higher employee engagement and productivity. A unified workspace eliminates constant application switching and provides a top user experience.
- Lower IT department workload. With self-service features, employees can find necessary resources, launch workflows, and access documents without IT assistance.
What is the role of enterprise application portals in ERP? Enterprise portals often integrate with major ERP systems such as SAP or Microsoft Dynamics 365. Through such integration, employees can access orders, invoices, client records, analytics, and financial reports directly from the portal without logging into separate systems.
This integration creates a single window view where operational data from ERP, documents from SharePoint, messages from Teams, and upcoming events from the calendar appear together in one interface. By bringing these elements together, enterprise portal software improves how smoothly business operations run and helps all departments work together effectively.
2. Differences Between Enterprise Portals and Small Business Solutions
The size and structure of a company directly influence its digital system requirements. Small businesses usually rely on simple portals or cloud-based tools for file sharing and communication. In contrast, corporations require more advanced and secure enterprise portal solutions with centralized management of data, users, and processes.
Enterprise portals are not just websites or document repositories. They are integrated platforms that connect dozens of business apps, process automation workflows, analytics, and access control. Such solutions form the digital basis of the organization, providing coordinated work across departments.
The main differences between enterprise portals and small business portals lie in their scale, flexibility, and level of control:
- In small businesses, digital tools are usually task-specific, focusing on file sharing, news publishing, or small project management.
- In large enterprises, the portals are a part of a broader ecosystem connecting multiple branches, suppliers, and clients through a single platform.
Enterprise Portal vs Small Business Portal
| Parameter | Enterprise Portal | Small Business Portal |
| Scalability | Designed for thousands of users and high-volume data. Can expand globally across departments and subsidiaries. | Limited scalability; effective for small teams and short-term collaboration. |
| Security | Advanced data protection, role-based access, compliance with corporate policies and regulations. | Basic access control; often relies on cloud service security. |
| Customization | Highly configurable and adaptable to complex business workflows. | Minimal customization, suitable for simple use cases. |
| Integrations | Deep integration with ERP, CRM, HR, and BI systems such as Microsoft 365, SAP, or Dynamics 365. | Limited integrations, often through built-in third-party plugins. |
| Content Management | Centralized document libraries with version control, workflows, and metadata. | Basic file storage and sharing features. |
| Support and Administration | Managed by IT professionals with defined governance and maintenance policies. | Usually self-managed or supported by the cloud provider. |
| Reporting and Analytics | Built-in dashboards and advanced analytics tools across departments. | Basic reporting, sometimes absent or manual. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment but long-term efficiency and ROI. | Lower cost, suitable for startups or small organizations. |
Enterprise portals are built with a long-term vision. They are not limited to storing data but serve as the core of a company’s infrastructure, supporting automation and cross-department collaboration. With their consistency and detailed control, enterprise web portals enable organizations to adapt quickly to market changes and expand their operations in no time.
Small business portals, on the other hand, offer task-specific solutions that work well in the early growth stages but are not designed for large-scale operations. As companies grow, such systems may struggle to handle increasing volumes of data and users.
For example, a small creative agency might use Google Workspace or Notion as a collaborative portal for exchanging documents and tracking tasks. Meanwhile, a corporation with thousands of employees would deploy an enterprise portal based on Microsoft SharePoint, where documents, reports, tasks, calendars, and analytics are available within one secure system.
In the enterprise environment, manageability and unified data control are the most important characteristics. When dozens of departments and hundreds of users interact with different types of information, the system must provide traceability and security of every action. This is where enterprise portals give a foundational advantage, turning dispersed tools into a single ecosystem.
3. Implementation Stages and Best Practices
3.1 Key Stages of Implementation
How to implement an enterprise portal effectively? Successful deployment requires a strategic approach. It should combine technical decisions with business alignment and user engagement. Below are the essential stages for a smooth and efficient implementation.
1. Analysis of business requirements and defining portal goals
At the first stage, organizations analyze their existing business processes and define the challenges the enterprise portal should address. These may include:
- improving communication between departments;
- improving knowledge and document management;
- automating routine operations such as approvals, reporting, and alerts;
- creating a single access point for corporate apps and analytics.
You should also involve department heads early in this process to identify the most critical use cases, such as an HR portal, a sales collaboration portal, or a knowledge hub. This way you make sure the enterprise portal software meets real operational needs.
2. Choosing the platform and deployment model
The choice of platform should depend on company scale, security requirements, and integration needs with existing solutions. Typical deployment models include:
- Cloud-based deployment (for example, SharePoint Online) – ideal for distributed teams and hybrid work models; reduces infrastructure costs and is easy to maintain.
- On-Premises deployment – suited for organizations with strict data security and compliance regulations.
- Hybrid deployment – combines the flexibility of the cloud with the control of local storage, so that sensitive data remains on-premises.
3. Defining roles and access policies
Clear access management is important for enterprises. The portal structure usually reflects both company hierarchy and information sensitivity. Access levels are configured:
- by departments (Finance, Marketing, HR, Sales);
- by roles (C-levels, managers, employees, partners);
- by data types (confidential, internal, public).
Such granular control makes sure users only see information relevant to their duties while protecting sensitive data.
4. Integration with ERP, CRM, Microsoft 365, and other systems
At this stage, the portal is connected with other enterprise applications to create a single ecosystem. Typical integration scenarios include:
- displaying real-time ERP reports directly in the portal dashboard;
- synchronizing tasks between CRM and SharePoint;
- embedding events from Microsoft Outlook and Teams;
- automating workflows through Power Automate.
Using ready-made connectors and add-ons from Virtosoftware significantly accelerates these integrations, reducing manual configuration time while increasing usability.
5. Employee training and change management
Implementing an enterprise portal is not only a technical transformation but also an organizational one that requires user adaptation. For successful adoption, it is recommended to prepare a structured education plan, including:
- short video tutorials and guides on features;
- webinars and Q&A sessions;
- appointing “digital ambassadors” within each department who help colleagues learn and collect feedback.
Employee engagement directly influences the success of the rollout. Even the most advanced enterprise solutions will not generate value unless users actively integrate them into their daily work.

3.2 Best Practices for Implementation
For a successful enterprise portal deployment and adoption, companies should follow several best practices. These approaches help minimize risks and increase user engagement from the very beginning.
- Start with a pilot project.
Begin implementation with a single department or a specific business process. A pilot allows companies to test interface, evaluate integration quality, and check workflow logic before scaling the solution company-wide. - Engage key users from the start.
Employees who participate in portal testing and feedback become advocates for the solution. Their involvement helps to make sure that system meets user needs and encourages faster adoption. - Use out-of-the-box solutions to speed up deployment.
Pre-built applications, such as VirtoSoftware apps for SharePoint, help implement essential functionality like task visualization, reminders, and calendar sync without developing custom apps from scratch. This significantly reduces time and implementation costs. - Expand functionality gradually.
Avoid rolling out all features at once. Start with the core elements—document libraries, calendars, and task lists—and add other features such as dashboards, workflows, or chatbot support as user adoption grows. - Ensure continuous feedback collection.
Conduct employee surveys and focus groups after each rollout phase to gather feedback on design and usability. Regular user input helps in making improvements that increase efficiency. - Monitor portal effectiveness regularly.
Measure performance indicators such as user engagement, workflow automation rates, and time saved in daily operations. These metrics help assess the return on investment (ROI) and guide further optimization of the enterprise portal software.
These best practices make enterprise portal implementation not just an IT project, but a strategic transformation. When aligned with user expectations, the portal becomes a vital part of the company’s workplace, driving better collaboration and productivity.
4. Use Cases and Implementation Results
Enterprise portals are widely used across industries for better data management and collaboration. Below are some examples of how organizations use enterprise portal solutions to achieve measurable improvements.
Centralized Data Management
A global manufacturing company deploys an enterprise portal based on SharePoint Online integrated with ERP and CRM systems. All documents, reports, and product specifications are stored in centralized libraries with version control. Access is managed through Azure Active Directory, allowing employees to view only the data relevant to their roles.
Using applications such as the Virto Alerts & Reminders App for Microsoft 365, the company automates notifications about report deadlines, equipment maintenance schedules, and data updates.
Results:
- Reduced duplication of documents and deleted outdated files.
- Improved accessibility of corporate data.
- Significant time savings for employees searching for documents.
Internal Communication and Collaboration
A multinational service provider introduces an enterprise web portal to strengthen communications between distributed offices. Built on Microsoft SharePoint and integrated with Microsoft Teams, the portal serves as a central hub for corporate news and updates. Employees can access discussion boards, event calendars, and task lists through a unified interface.
Using the Virto Calendar app, the organization combines updates from multiple channels and visualizes events from Teams and Outlook in one calendar view.
Results:
- Improved engagement across departments.
- Faster information flow between teams and branches.
- Increased employee participation in corporate initiatives.
Project Control, Reporting, and Approvals
A financial institution implements an enterprise portal to streamline project tracking and approval workflows. The system integrates SharePoint libraries for document management, Power Automate for workflow automation, and Power BI dashboards for real-time analytics. Managers can monitor project statuses, expenses, and metrics through interactive dashboards directly on the portal homepage.
Virto Kanban Board for Microsoft 365 helps visualize tasks and approval stages, so that all stakeholders stay informed of project progress.
Results:
- Reduced approval times for project documentation by up to 40%.
- Improved visibility into ongoing projects and resource allocation.
- Increased workflow efficiency across departments.
5. Enterprise Portal Based on Microsoft SharePoint
Microsoft SharePoint remains one of the most popular platforms for building enterprise portals thanks to its powerful combination of content management, collaboration tools, and enterprise-level security. With it, organizations of any size can create scalable digital workspaces that serve as the foundation for modern enterprise portals.
SharePoint seamlessly integrates with Microsoft 365, Teams, and Outlook, forming a unified working environment where employees can access documents, manage tasks, participate in discussions, and track updates – all from a single interface. Its flexible structure allows companies to develop customized solutions that reflect their needs and workflows.
👉 Learn more about Microsoft Digital Workplace >>>
Typical Use Cases
- Internal corporate portals (intranet).
Companies use SharePoint intranet portals to centralize internal communication, distribute policies and news, manage documents, and foster a strong corporate culture. - HR portals for employees.
HR departments build employee portals on SharePoint to automate onboarding, training, and internal requests, giving transparent access to resources such as vacation policies, benefits, and learning materials. - Customer and partner extranet portals.
Extranet sites assist with secure collaboration with partners, clients, and suppliers. They allow external users to exchange files, track project status, and communicate with company teams while maintaining strict access control.
SharePoint Online vs SharePoint On-Premises
Both versions of SharePoint can serve as the foundation for an enterprise portal, but they differ in deployment and management models:
| Aspect | SharePoint Online | SharePoint On-Premises |
| Deployment | Hosted in Microsoft 365 cloud, managed by Microsoft. | Installed on the company’s servers and managed internally. |
| Maintenance | Automatic updates and scalability without local infrastructure. | Greater control over configuration, updates, and data storage. |
| Security | Cloud-based compliance managed by Microsoft Security Center. | Local data control, suitable for strict regulatory requirements. |
| Integrations | Deep integration with Microsoft 365, Teams, and OneDrive. | Can integrate with legacy enterprise systems. |
| Customization | Rapid configuration using ready-made web parts and apps. | Broader flexibility for custom development and complex workflows. |
Organizations choose between SharePoint Online and SharePoint On-Premises depending on their infrastructure, compliance, and integration needs. Some opt for a hybrid model that combines the scalability of the cloud with the security and control of local data storage.
In all cases, SharePoint provides the essential basis for a robust enterprise portal system—combining collaboration, automation, and governance into a single platform. Its compatibility with Virtosoftware solutions further extends its functionality, empowering companies to build feature-rich environments tailored to their digital transformation goals.
6. Enhancing Enterprise Portal Capabilities with VirtoSoftware
VirtoSoftware solutions extend Microsoft SharePoint’s functionality, helping companies automate processes and visualize data. These tools transform an enterprise portal into a digital workspace where employees can monitor projects, manage documents, and communicate, all within the familiar Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
6.1 Tools for SharePoint Online and Microsoft 365
Virto Calendar App for M365 and Teams
Virto Calendar App consolidates multiple calendars—including those from SharePoint lists, Outlook events, and Microsoft Teams—into one interactive view. It helps employees plan meetings, track company events, and coordinate team schedules. The app supports color coding, filtering by departments or event categories, and integration directly within Teams or the SharePoint page. Managers can quickly identify overlapping events or free slots for team-wide planning.
Key benefits: unified scheduling, visual event planning, improved time coordination, integration with Teams.
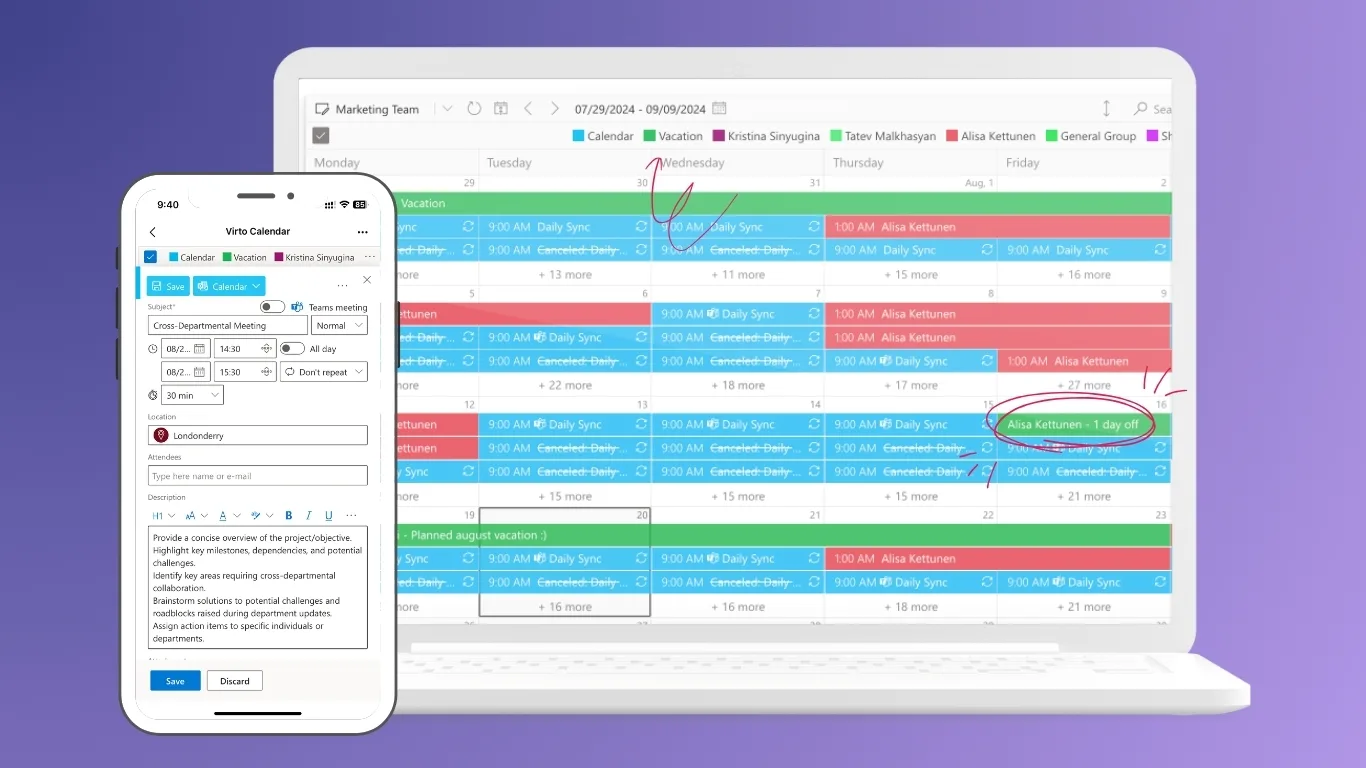
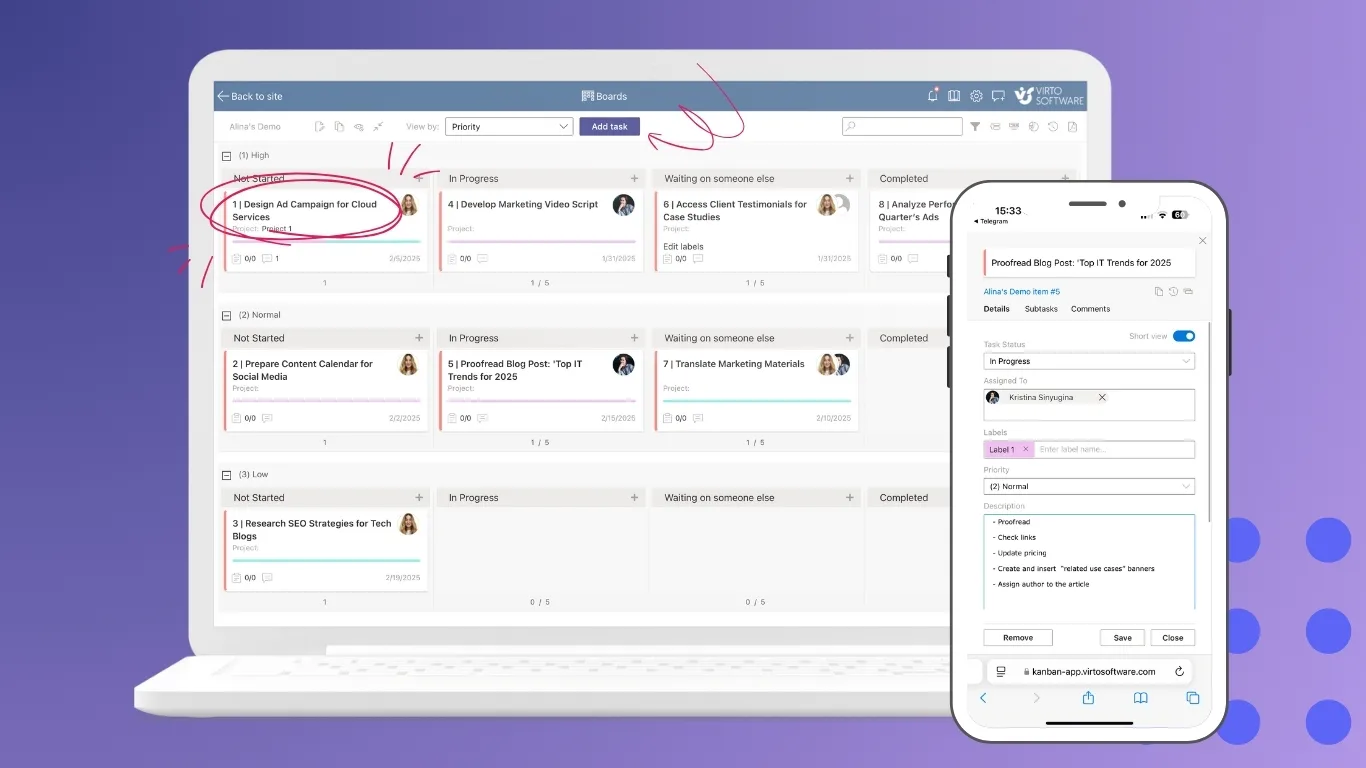
Virto Kanban Board App for M365 and Teams
Virto Kanban Board App provides visual task management suited for project tracking and agile workflows. Users can create task cards, assign owners, set due dates, and move cards between columns representing workflow stages. The app integrates with Microsoft Lists and SharePoint libraries, enabling automated synchronization of tasks and statuses. It enhances transparency across departments and supports drag‑and‑drop functionality for intuitive updates.
Key benefits: visual workflow control, real-time task monitoring, improved project transparency, integration with Teams.
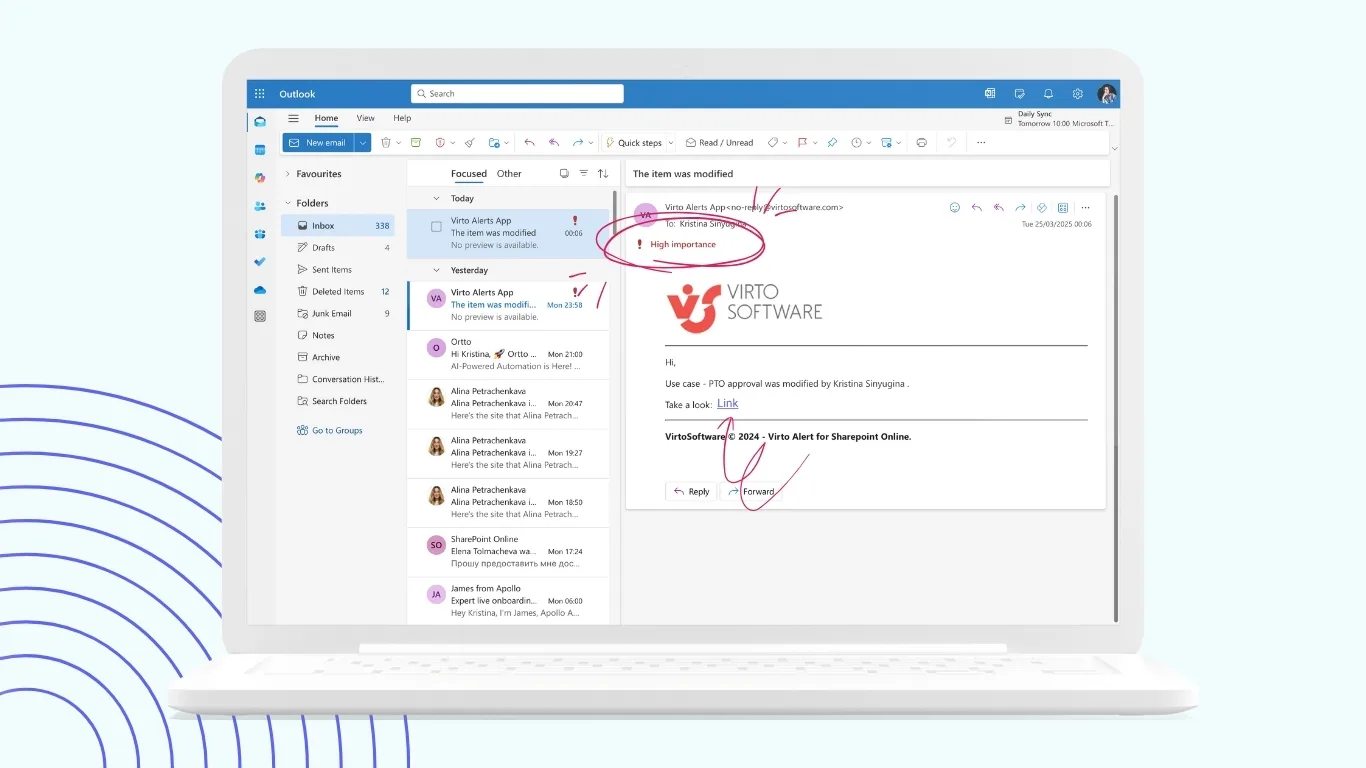
Virto Alerts & Reminders App for M365
Virto Alerts & Reminders App automates the creation of notifications and reminders for documents, tasks, and deadlines. It supports multiple delivery methods—email, Teams messages, or dashboard pop-ups—and allows users to configure custom rules for recurring alerts. For example, employees can receive reminders before report submission dates, policy updates, or contract renewals.
Key benefits: proactive communication, reduction of overdue tasks, and document control.
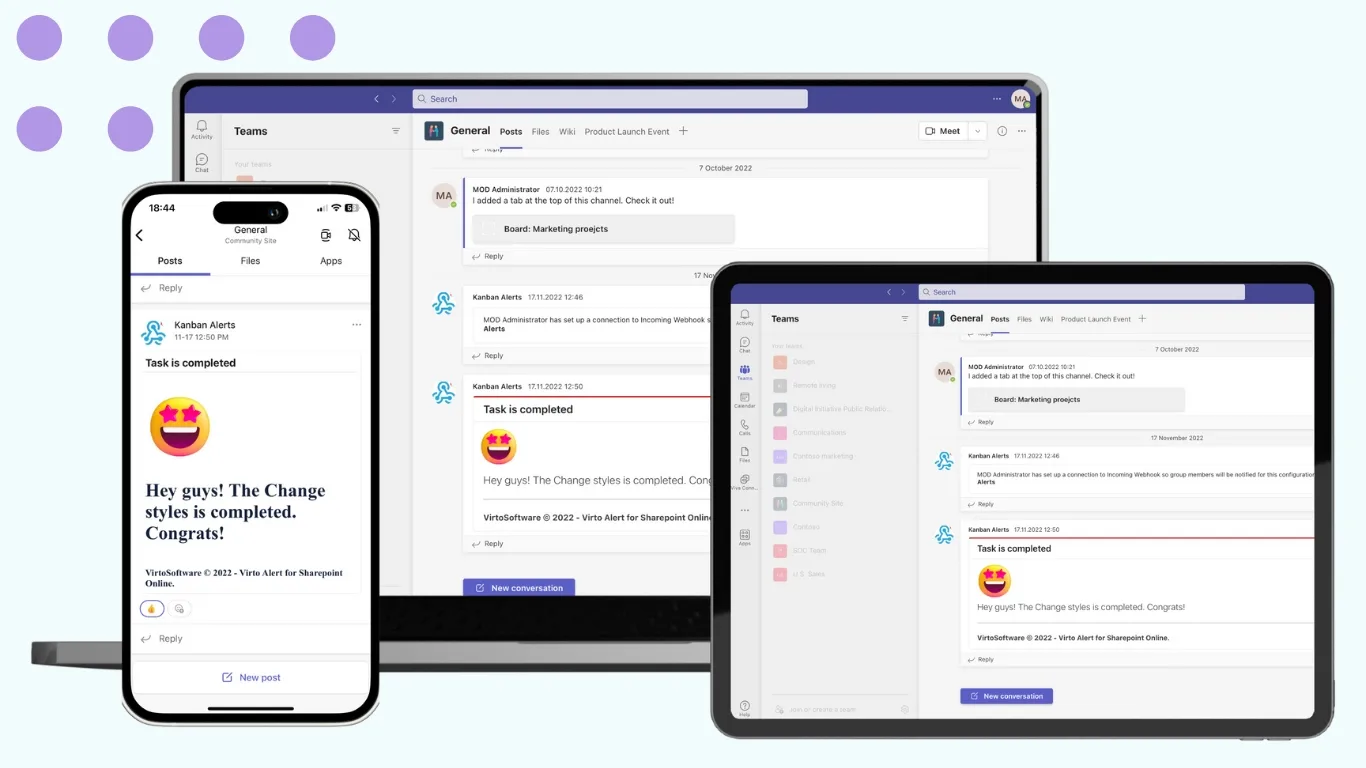
Virto Notifications & Reminders App for Teams
An advanced version of the alert system built directly into Microsoft Teams. It delivers personalized notifications to users and groups, ensuring employees stay informed about upcoming events, meetings, and task changes. The app supports message templates, group notifications, and scheduling, making it ideal for enterprises and distributed teams.
Key benefits: centralized communication, consistent updates, and higher team engagement within Microsoft Teams.
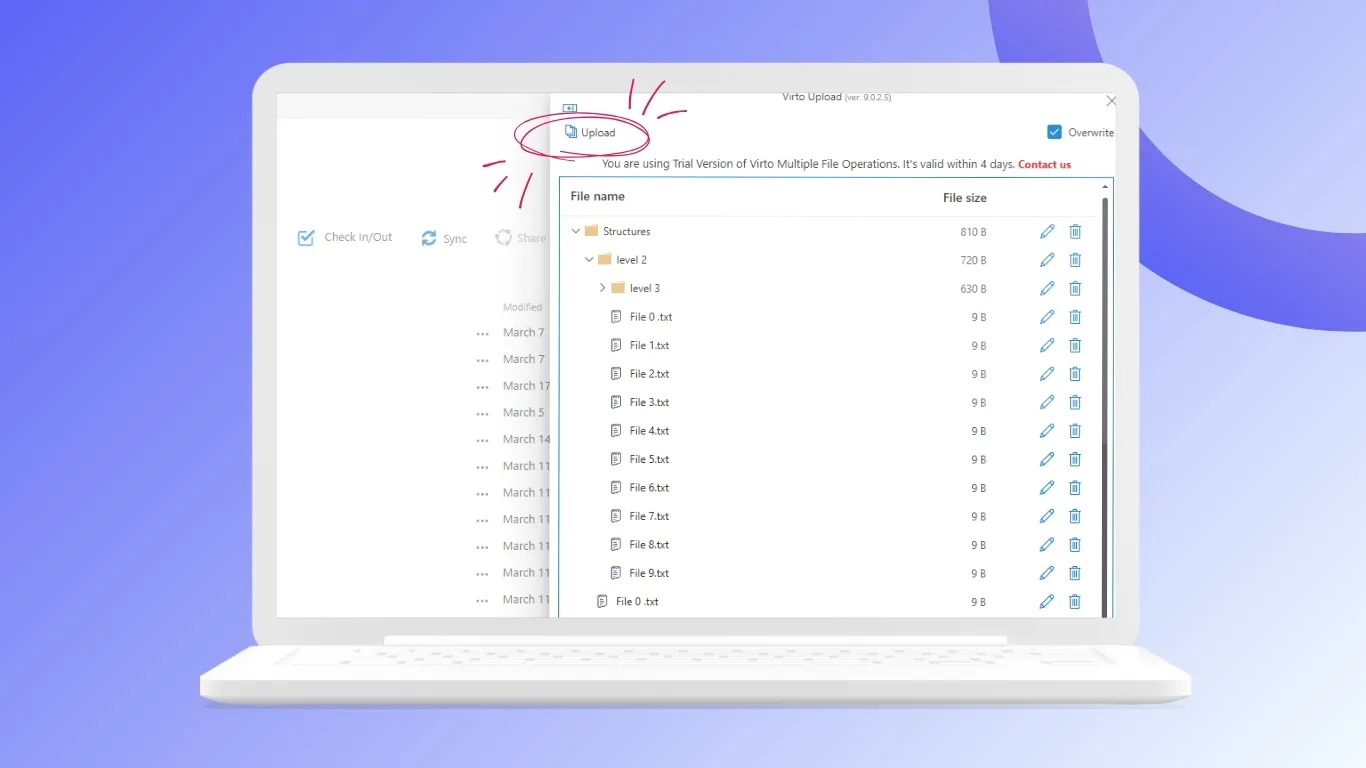
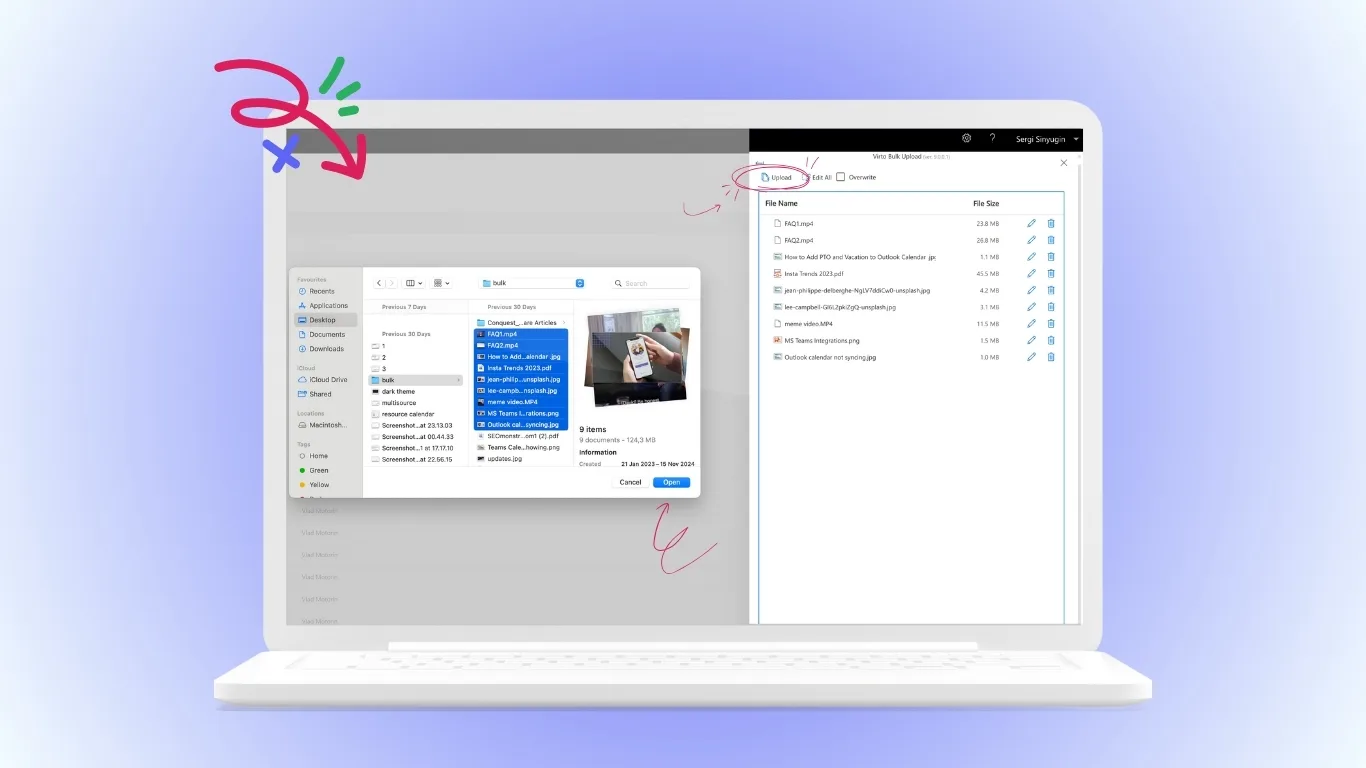
Virto Multiple File Upload App for Microsoft 365
This app simplifies bulk file management in SharePoint document libraries. Employees can upload multiple files simultaneously using drag‑and‑drop and automatically assign metadata during upload. Built-in duplicate detection prevents version conflicts, while mandatory metadata fields ensure consistent document classification. It is particularly useful for HR, finance, and legal departments dealing with large volumes of documentation.
Key benefits: faster uploads, cleaner document organization, and improved data accuracy.
Together, these tools transform SharePoint Online into a flexible enterprise portal that unites data visualization, task automation, and collaboration, helping companies maintain productivity at scale.
6.2 Tools for SharePoint On‑Premises
Virto Multiple File Operations
This solution automates mass document actions—such as copying, moving, renaming, and deleting—directly from SharePoint libraries. With its easy interface, users can process hundreds of documents at once without IT assistance. Virto Multiple File Operations simplifies large-scale content restructuring, making it essential for document-heavy departments like HR, legal, or operations.
Key benefits: time savings, reduced manual errors, and simplified document administration.
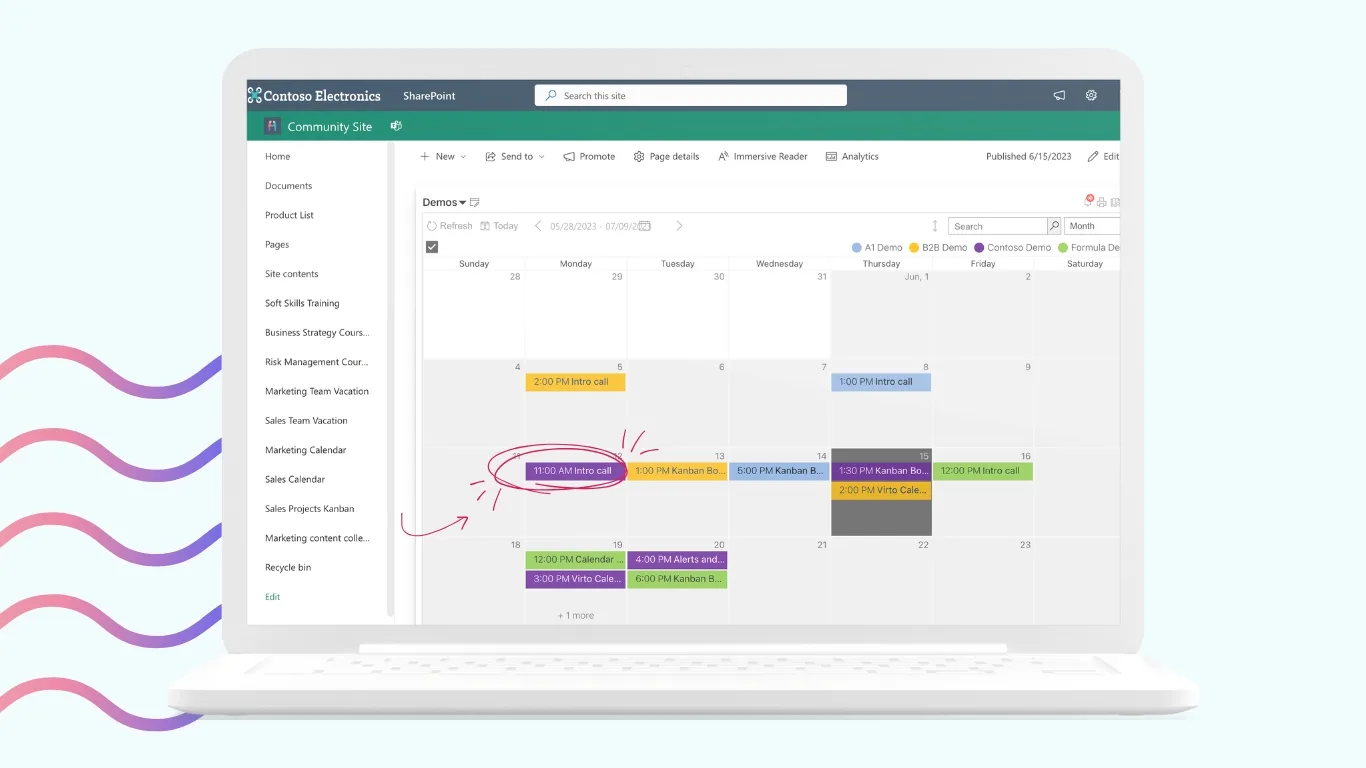
Virto Calendar Web Part
The on-premises Virto Calendar integrates seamlessly with Outlook and Exchange, displaying shared events, meetings, and task deadlines on one interface. It allows color tagging, filtering by departments, and drag‑and‑drop event editing. Virto Calendar Web Part improves time management and makes sure all stakeholders remain informed about activities and milestones.
Key benefits: improved coordination, visual scheduling, and easy event planning.
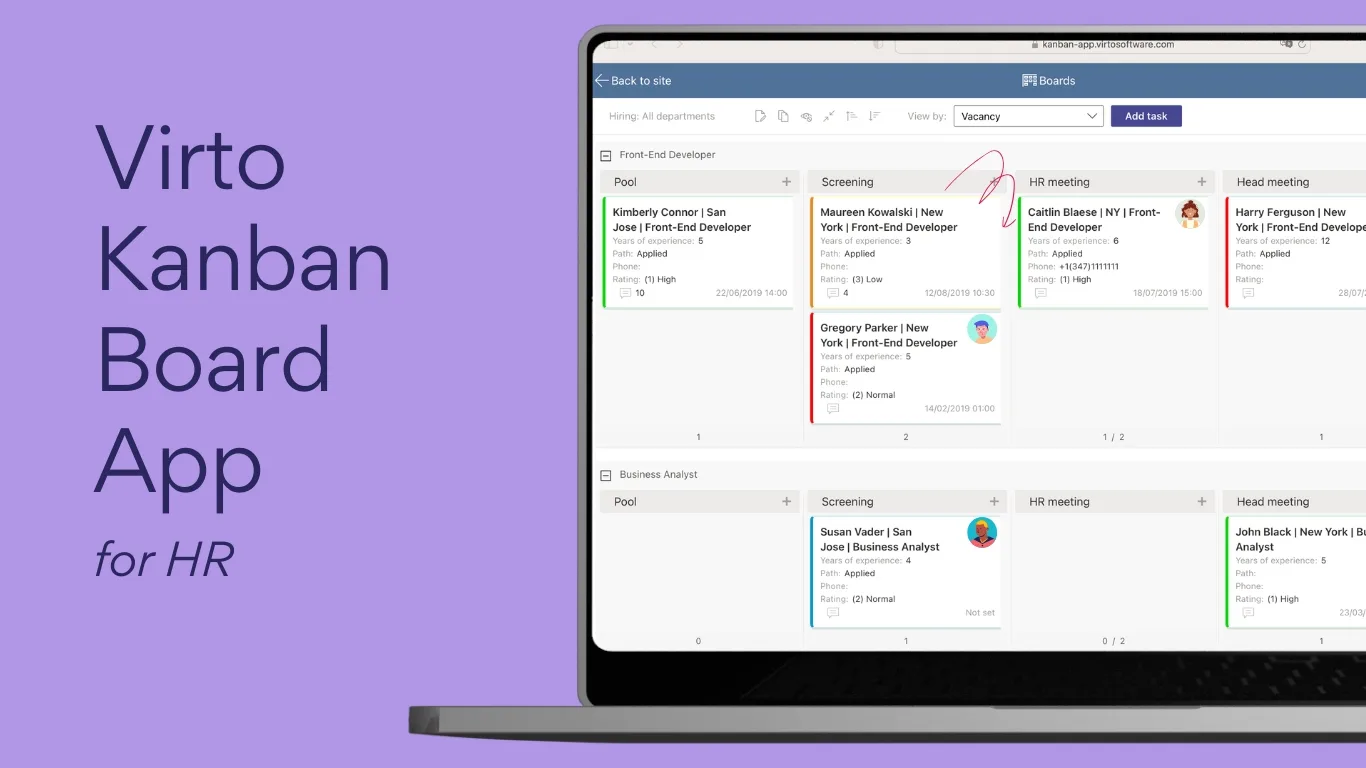
Virto Kanban Board Web Part
Designed for companies with local infrastructure, Virto Kanban Board web part brings agile project management to SharePoint On‑Premises. Teams can visualize project stages, assign tasks, set priorities, and track overall progress in real time. It supports filtering by users, departments, or deadlines, and helps management identify workload imbalances or bottlenecks in workflows.
Key benefits: project transparency, improved coordination, and intuitive visual management.
Example in practice:
An HR portal built on SharePoint On‑Premises can combine the Virto Calendar Web Part with the Kanban Board to manage recruitment workflows and events. Recruiters can post open positions as Kanban tasks, schedule interviews in the calendar, and receive automatic reminders about candidate evaluations. This integration improves HR team efficiency, ensures timely communication, and centralizes all hiring data in one controlled environment.
Conclusion
An enterprise portal serves as the strategic foundation for digital transformation in large companies. It unifies communication, data management, and workflow automation within a single environment, helping businesses operate more collaboratively. When implemented correctly, an enterprise portal not only speeds up daily operations but also strengthens corporate culture and accelerates overall business growth.
Microsoft SharePoint remains one of the most flexible, scalable, and secure platforms for building enterprise portals. Its integration with Microsoft 365 and compatibility with both cloud and on‑premises infrastructures make it a universal choice for organizations of any size and industry.
To unlock even greater value, companies can improve SharePoint with VirtoSoftware solutions. These products expand standard SharePoint functionality, adding visual workflow management, intelligent notifications, automated reminders, and advanced document handling. Together, SharePoint and VirtoSoftware empower enterprises to create intelligent, user‑friendly, and fully tailored portals that align with their goals and support continuous innovation.